As of last May, GDPR is now in effect across the entirety of the EU after 4 years of crafting in order to improve and standardise data security in an era increasingly prone to cyber attacks and malicious hacking. Due to the standardisation of practice across the various constituent nations compromising the Union, those organisations found to be guilty of non-compliance and enabling a breach will face harsh penalties for failing to secure user data.
Under Article 30 of the GDPR legislation, organisations consisting of 250 or more employees are those who have the most to do to in accordance with the new practices. A dedicated Data Protection Officer will become a mandatory member of staff tasked not only with protecting sensitive information, but also with ensuring that all data is collected lawfully and with active user content for a lawful and legitimate interest.
What is considered to be personal data has also been expanded and as well as that which was classified under the existing Data Protection Act, now also includes a user’s IP Address, as well as their economic, cultural and mental health information.
Individual users now have the right to access their data at ‘reasonable’ intervals and can request to see what details of theirs are being stored on record. They may know the intent behind the organisation doing so, can request amendments be made, and if they want to, can request to have it deleted permanently.
For further information on getting GDPR compliant, check out this infographic on the matter:
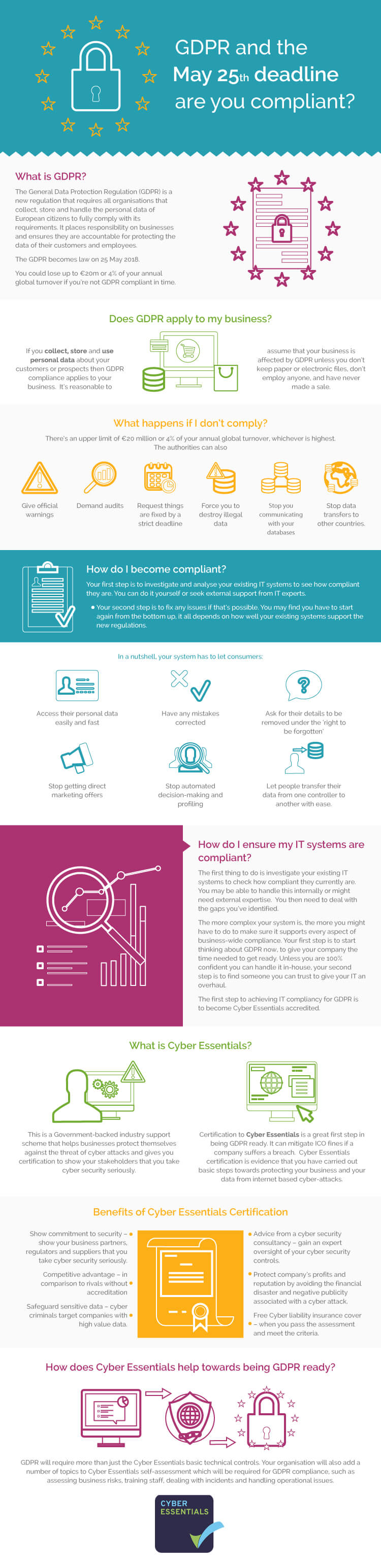
GDPR Infographic – Are You Compliant?
Reference: Fox, J. (2018) GDPR Infographic – Are You Deadline Compliant. Available at: https://cheekymunkey.co.uk/gdpr-infographic-am-i-compliant-cyber-essentials/ [Accessed: 14 June 2018]